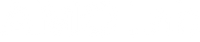
미주신경은 부교감신경계의 핵심 부분으로, "휴식 및 소화" 시스템으로도 알려져 있습니다. 이 신경은 호흡, 소화 기능 및 심박수에 영향을 미치며, 정신 건강에 큰 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.

장수와 건강의 지름길
노화는 항상성을 유지하는 신체의 능력, 즉 스트레스 요인에 대한 반응으로 "자가 조정" 또는 '자가 안정화' 하는 우리 신체 능력의 감소가 원인입니다. 우리의 도전은 미주신경의 심장 분지를 자극함으로서 자율신경계의 불균형을 교정하여 더 건강한 삶을 영위하게 하며, 노화를 지연시키는 혁신적인 생체전자기술을 통해 인간 고유의 타고난 능력인 항상성을 회복시키는 것입니다.

미주신경에 모든 것이 있습니다
만성 스트레스, 걱정 또는 수면 부족은 우리의 면역 체계에 부정적인 영향을 미치고 균형을 무너뜨리고 질병의 발병 또는 악화 위험 을 높입니다.
미주신경은 인체에서 가장 긴 신경으로 자율신경계의 부교감신경의 일부이며, 면역 방어 메커니즘의 지휘자입니다. 미주신경의 미주톤을 활성화하여 부교감신경이 제대로 작동하면 고혈압, 심장병 및 뇌졸중의 위험이 줄어듭니다. 소화 대사를 증가시켜 장에 좋으며, 편두통을 감소시킵니다. 그것은 또한 당신이 더 건강하게 나이를 먹을 수 있을 뿐만 아니라 개인의 사망 위험은 물론 약물 치료 또는 병원 방문의 필요성도 낮아집니다.

미주신경
자율신경계의 활동을 조절하기 위해 미주신경을 자극한다는 아이디어는 100년 이상 추구되어 왔습니다. 미주신경은 부교감신경 섬유를 심장으로 전달하는데, 그 신호는 심박수를 늦출 수 있습니다. 또한 미주신경 자극 효과는 수면과 스트레스를 개선할 뿐만 아니라 전반적인 신체 기능을 강화할 수 있습니다.미주신경의 기능 장애는 심장과의 관계로 인해 매우 위험할 수 있습니다. 한편, 미주 신경 자극은 간질을 비롯한 다양한 장애에 잠재적으로 유용하다는 것이 입증되었습니다.

Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) has two major efferent pathways, sympathetic and parasympathetic which innervate and affect all the organs in the body. The structure of the autonomic nervous system with numerous neurotransmitters and synapses allows for the flexible control of organ functions and the maintenance of systemic blood pressure and body temperature.

Autonomic Disorders
Autonomic dysfunction can make us feel old and sick, whilst keeping us from enjoying our basic quality of life. Autonomic Dysfunction means that many systems in our body stop working properly and as a result we can feel tired and dizzy, have headaches, and are increasingly unable to eat or digest food, use the bathroom as normal, get a good night’s sleep, or have sexual intercourse. Autonomic dysfunction is the key to chronic pain, chronic fatigue, persistent hunger, insomnia, emotional regulation, blood pressure and blood sugar regulation, depression, anxiety, panic attacks and PTSD (posttraumatic stress disorder).
Recent studies have found significant evidence that Vagus Nerve stimulation (VNS) may be a potential adjunct therapy for COVID-19.

Although there is no specific treatment for COVID-19, drug repurposing has made it possible to identify drugs that may be effective against the disease. Drugs that can mainly inhibit cytokine release and recover inflammatory control are being studied.
New studies have been published focusing on vagus nerve stimulation as a potential COVID-19 therapy. This approach manipulates the activity of cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathways, and recently, this therapeutic strategy has become an important approach for the treatment of inflammatory diseases and sepsis.

A recent study by the Mayo Clinic reported that up to 63% of patients after the COVID-19 infection have autonomic dysfunction with specific symptoms. When the autonomic nervous system is always in fight-or-flight mode (meaning that it is not relaxed), it is out of balance. This loss of balance underlies the immune dysregulation and runaway inflammation associated with chronic stress, and appears to play a role in severe cases of COVID-19.

COVID-19 decreases parasympathetic activity and increases sympathetic activity, which leads to catecholamine release. The secretion of catecholamines increases blood flow and metabolism and stresses the heart. Reduced parasympathetic activity may reduce the vagal anti-inflammatory effect leading to a cytokine storm.
The Vagus Nerve, a neural network that connects the brain and immune system to the heart, intestines and other organs, controls parasympathetic activity in the autonomic nervous system. When the Vagus Nerve is activated, it acts as a brake on stress and all immune-stimulating effects in the body. Vagus Nerve stimulation has also been shown to suppress inflammatory responses, and may be useful in regulating lung failure and hyperimmune responses.